Ordered Pairs on the Coordinate Plane
Basics on the topic Ordered Pairs on the Coordinate Plane
Ordered Pairs – Introduction
When you think about finding a location, you probably think of a map. In mathematics, we use a similar concept to find locations, but we call them ordered pairs and the "map" is known as the coordinate plane. Grasping the concept of ordered pairs is essential in math because it's the foundation of graphing and understanding relations between numbers in a visual way.
Understanding Ordered Pairs – Definition
An ordered pair is a pair of numbers used to locate a point on a coordinate plane. The first number is called the x-coordinate, and the second number is the y-coordinate.
Ordered pairs follow a specific format: (x, y). This format tells us the exact position of a point relative to the origin, where the x-axis and y-axis intersect.
Rules for Ordered Pairs:
- The first coordinate, x, indicates horizontal movement from the origin.
- The second coordinate, y, indicates vertical movement from the origin.
- Negative x values mean movement to the left, and negative y values mean movement down.
Plotting Ordered Pairs – Example
Let's plot the point (3, -2) on the coordinate plane. Remember, the first number is the x-coordinate, and the second number is the y-coordinate.
- Start at the origin (0,0).
- Move 3 units to the right, as the x-coordinate is positive.
- Move 2 units down since the y-coordinate is negative.
- Place your point. You've now successfully plotted the point (3, -2).
Graphing Equations Using Ordered Pairs – Guided Practice
Consider the equation y = 2x + 1. To graph this equation, we need to find ordered pairs that satisfy it.
Understanding Quadrants and Axes – Explanation
The coordinate plane is divided into four sections known as quadrants. These quadrants are labeled with Roman numerals:
| Quadrant | Description |
|---|---|
| Quadrant I | Top right, where both x and y are positive. |
| Quadrant II | Top left, where x is negative, and y is positive. |
| Quadrant III | Bottom left, where both x and y are negative. |
| Quadrant IV | Bottom right, where x is positive, and y is negative. |
The axes themselves—x-axis and y-axis—are also important. They divide the plane into quadrants and are used as reference lines to determine the coordinates of points.
Slope Calculation – Summary
Key Learnings from this Text:
- An ordered pair tells us the position of a point on the coordinate plane.
- The x-coordinate is the first number, indicating horizontal movement.
- The y-coordinate is the second number, indicating vertical movement.
- The quadrants help us determine the sign of the coordinates.
- Distance and midpoint formulas are useful for finding the length and center between two points.
- The slope measures the steepness of a line on the graph.
If you're curious to delve deeper into the world of coordinates and want to master graphing, check out our interactive practice problems and engaging video content!
Ordered Pairs – Frequently Asked Questions
Transcript Ordered Pairs on the Coordinate Plane
Luis has a new robot, except he has one problem. He needs to understand how his robot moves to different places from its starting location on a specially programmed map. To do this, he will learn about ordered pairs on the coordinate plane. You may have seen graphs like this before, with an X and Y axis, called a coordinate plane. In this graph, both the X axis and the Y axis act like number lines, and intersect at the zero. Let's construct a new type of coordinate plane step by step. Zero is what we call the origin point of the coordinate plane, which is the central point. On the X axis, going to the right are positive values, and going to the left are negative values. On the Y axis, going upwards are the positive values, and going downwards are the negative values. You might notice that the X axis and the Y axis intersection divides the graph into four. These are known as quadrants. Starting from the top right quadrant, and going counter-clockwise we have quadrant one, quadrant two, quadrant three, and quadrant four. Now let's look at the signs for each quadrant. Quadrant one has positive X and Y values. Quadrant two has negative X and positive Y values. Quadrant three has negative X and Y values. Quadrant four has positive X and negative Y values. The values in each ordered pairs tell us where to plot them and in which quadrant. An ordered pair is a pair of numbers that represent a point on the coordinate plane. The first value tells us the position along the X axis, and the second value tells us the position along the Y axis. The ordered pair for the origin is always zero, zero. Luis' robot is programmed with the ordered pair of three, four, so we need to find where it will end up. Both the X value and the Y value are positive. This means the robot is in quadrant one, because you will go right on the X axis, and up on the Y axis. Let's look at another example. This time, Luis' robot is programmed to end up at negative two, six. Which quadrant is the robot in? Since the X value is negative, and the Y value is positive, the robot is in quadrant two. Luis' robot is programmed one final time, and will end up at the ordered pair three, negative three. Which quadrant is the robot in? Since the X value is positive, and the Y value is negative, the robot is in quadrant four. Luis finally understands the way his robot is programmed to move, so let's summarize! In summary, a coordinate plane has four quadrants. The signs of the values in an ordered pair indicate which quadrant the point is located in. Quadrant one has positive X and Y values. Quadrant two has negative X and positive Y values. Quadrant three has negative X and Y values. Quadrant four has positive X and negative Y values. Well, Luis now understands his robots map, but it sure would help if he remembered to charge it first!
Ordered Pairs on the Coordinate Plane exercise
-
Identify the quadrants.
HintsThe coordinate point is written as the $x$ coordinate first and the $y$ coordinate second. $(x, y)$
The axes are set out like a number line with positive and negative numbers.
$(x, y)$
- $x$ is the horizontal axis
- $y$ is the vertical axis
We can see these example points are written:
- A $= (3, 2)$
- B $= (-2, 5)$
- C $= (-2, -2)$
- D $= (3, -5)$
Solution- In Quadrant $1$ the $x$ and $y$ axis are positive numbers, so the coordinates are $(+, +)$.
- In Quadrant $2$ the $x$ axis is negative and $y$ is positive, so the coordinates are $(-, +)$.
- In Quadrant $3$ the $x$ and $y$ axis are negative numbers, so the coordinates are $(-, -)$.
- In Quadrant $4$ he $x$ axis is positive and $y$ is negative, so the coordinates are $(+, -)$.
-
Find the quadrant.
HintsThe quadrants are laid out like this:
When a coordinate point has a negative $x$ and a negative $y$ we are moving left and down.
Point $(-4, -3)$ has both negatives $(-, -)$. This means we move left for $4$ and down for $3$.
Solution$(-4, -3)$ is in quadrant $3$ because both the coordinates are negative numbers $(-, -)$.
We move left for $4$ and down for $3$, see diagram.
-
Find the coordinate point.
HintsTo find each point:
- first move horizontally for the $x$ coordinate.
- second move vertically for the $y$ coordinate.
Here is how we found coordinate A.
- First we moved horizontally $3$ to get the $x$ coordinate.
- Second we moved vertically $5$ to get the $y$ coordinate.
- We would write this $(3, 5)$.
Solution- A $= (3, 5)$ $3$ right, $5$ up
- B $= (5, -3)$ $5$ right, $3$ down
- C $= (3, -5)$ $3$ right, $5$ down
- D $= (-3, -5)$ $3$ left, $5$ down
- E $= (-5, 3)$ $5$ left, $3$ up
-
Find the mistake.
HintsThe coordinate point is written across first, then up or down next.
It looks like this $(x, y)$.
For example, $(4, -5)$ is $4$ moves to the right from the origin and $5$ moves down from the origin.
This point is $(-3,8)$ because the $3$ is to the left, so it’s $-3$ and the $8$ is up, so it is $+8$.
The correct point is $(-3,8)$.
SolutionThe mistake was at $(7, -5)$, it was $7$ left and $5$ down which is $(-7, -5)$.
The correct ones are:
- $(3, 2)$, $3$ right and $2$ up
- $(4, -2)$, $4$ right and $2$ down
- $(-2, -2)$, $2$ left and $2$ down
- $(-3, 8)$, $3$ left and $8$ up
-
Find the coordinate.
HintsWe write coordinates by counting the $x$ or first number across/horizontally, then the $y$ or second number up or down/vertically.
$(x, y)$
The $x$ coordinate is $4$ to the right and the $y$ is $2$ down.
As a check we know it is in Quadrant $4$, so the coordinates should be in the order $(+, -)$.
Solution- $(4, -2)$
- For the $x$ coordinate (the first number), we move $4$ across/horizontally.
- For the $y$ coordinate (the second number), we move $2$ down/vertically.
- As a check we know it is in quadrant $4$ which has $(+, -)$ coordinates.
-
Form a square using the points.
HintsA square has $4$ vertices of $90^\circ$ and $4$ sides of equal length.
We can see in this example that the red cross forms the square with the other points making the sides the same length and each vertex $90^\circ$, a right angle.
SolutionThe correct answer is $(2, 7)$.

Even and odd numbers

Divisibility Rules - 3, 6, 9

Divisibility Rules - 7

Divisibility Rules - 4, 5, 8, 10

Prime Numbers
Integers and their Opposites
Least Common Multiples
Prime Factorization
Adding and Subtracting Rational Numbers on a Number Line
Ordering Rational Numbers

Cube Roots

Rational and Irrational Numbers
Ordered Pairs on the Coordinate Plane
Finding the Greatest Common Factor
Adding and Subtracting Decimals
Comparing Fractions
Equivalent Fractions
Simplifying Fractions
Temperature Conversion
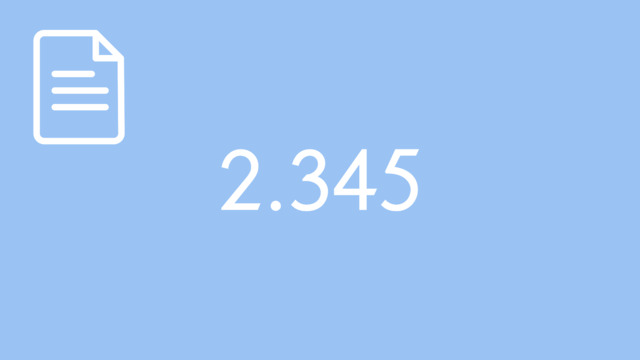
Decimal Expansions
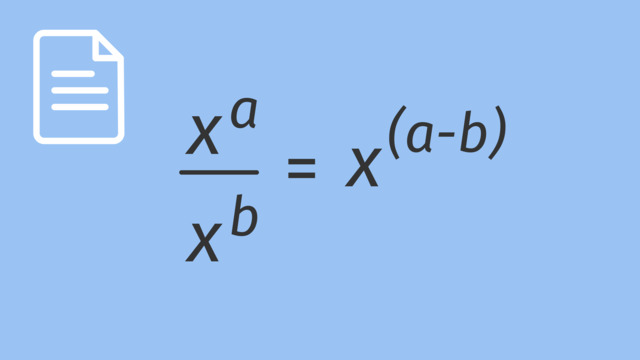
Division with Exponents
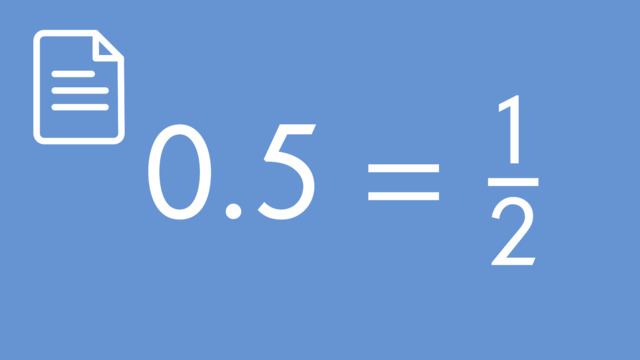
How to Convert Decimals Expansions
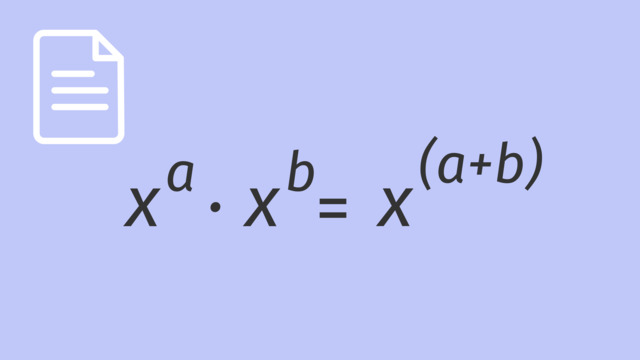
Multiplication with Exponents
Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers

Multiplying Mixed Numbers: Word Problems










