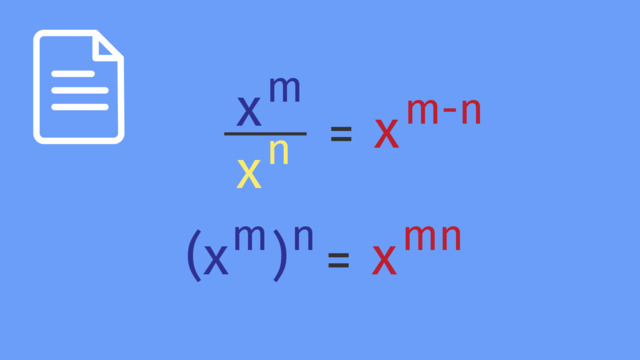Proofs of Laws of Exponents
- Proofs of Laws of Exponents
- Understanding Proofs of Laws of Exponents – Explanation
- Product of Powers
- Quotient of Powers
- Power of a Power
- Zero Exponent
- Negative Exponent

Basics on the topic Proofs of Laws of Exponents
Proofs of Laws of Exponents
In algebra, numbers written in exponential notation are used to represent repeated multiplication of the same number. Understanding and proving the laws of exponents is essential in mathematics, as they frequently appear in various calculations, from simple algebraic expressions to complex scientific formulas.
The laws of exponents are rules that describe how to handle exponential expressions, especially when multiplying, dividing, or raising powers to other powers.
Understanding Proofs of Laws of Exponents – Explanation
The laws of exponents include several rules, each crucial for simplifying and solving exponential expressions.
Product of Powers
Product of Powers: When multiplying powers with the same base, add the exponents.
Proof: Consider $a^{m} \times a^{n}$. Expanding this, we get $a \times a \times ...$ ($m$ times) multiplied by $a \times a \times ...$ ($n$ times). The total count of '$a$'s being multiplied is $m + n$, proving that $a^{m} \times a^{n} = a^{m+n}$.
| Example | Solution |
|---|---|
| Simplify $4^{3} \times 4^{2}$ | $4^{5}$ |
| Simplify $5^{2} \times 5^{3}$ | $5^{5}$ |
| Simplify $2^{4} \times 2^{2}$ | $2^{6}$ |
Quotient of Powers
Quotient of Powers: When dividing powers with the same base, subtract the exponent of the denominator from the exponent of the numerator. This concept is also fundamental to understanding division with exponents.
Proof: Consider $\dfrac{a^{m}}{a^{n}}$. Expanding, we get $\dfrac{a \times a \times ... (m \text{times})}{a \times a \times ... (n \text{times})}$. Canceling out the common '$a$'s, we're left with $m-n$ of them, so $\dfrac{a^{m}}{a^{n}} = a^{m-n}$.
| Example | Solution |
|---|---|
| Simplify $\dfrac{5^{7}}{5^{2}}$ | $5^{5}$ |
| Simplify $\dfrac{10^{6}}{10^{3}}$ | $10^{3}$ |
| Simplify $\dfrac{3^{8}}{3^{5}}$ | $3^{3}$ |
Power of a Power
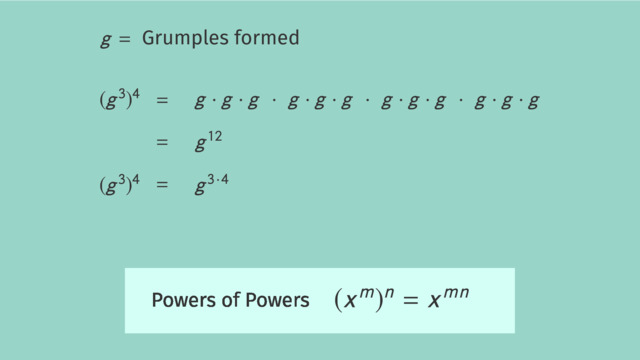
Power of a Power: When raising a power to another power, multiply the exponents. This principle not only applies to the powers of products and quotients but also to numbers in exponential form raised to a power.
Proof: Consider $(a^{m})^{n}$. Expanding the inner power, we have $a^{m} \times a^{m} \times ...$ ($n$ times). Each $a^{m}$ has '$m$' occurrences of '$a$', so in total, we have $m \times n$ occurrences, thus $(a^{m})^{n} = a^{mn}$.
| Example | Solution |
|---|---|
| Simplify $(3^{2})^{3}$ | $3^{6}$ |
| Simplify $(4^{3})^{2}$ | $4^{6}$ |
| Simplify $(2^{5})^{4}$ | $2^{20}$ |
The concept of numbers in exponential form raised to a power involves understanding how numbers expressed in exponential form can be further elevated by an additional power, a process that entails multiplying the exponent in the original expression by the new power applied.
Zero Exponent
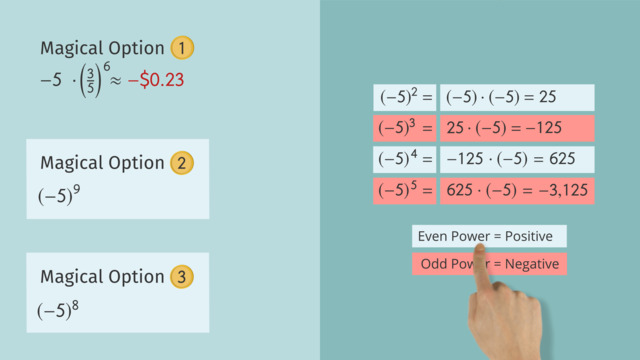
Zero Exponent: Any base raised to the power of zero equals one. This concept is closely related to numbers raised to the zeroth power.
Proof: Consider $a^{m} \div a^{m} = a^{m-m}$. According to the quotient rule, this equals $a^{0}$. Since $a^{m} \div a^{m} = 1$, it proves $a^{0} = 1$.
| Example | Solution |
|---|---|
| Evaluate $6^{0}$ | $1$ |
| Evaluate $4^{0}$ | $1$ |
| Evaluate $(-5)^{0}$ | $1$ |
These examples illustrate the Zero Exponent law, which asserts that any number raised to the power of zero equals one.
Negative Exponent
Negative Exponent: A negative exponent indicates the reciprocal of the base raised to the positive exponent. This principle is an essential part of understanding zero and negative exponents.
Proof: Consider $a^{-n}$. This can be written as $\dfrac{1}{a^{n}}$. Therefore, the negative exponent signifies an inverse relationship.
| Example | Solution |
|---|---|
| Evaluate $3^{-2}$ | $\dfrac{1}{3^{2}} = \dfrac{1}{9}$ |
| Evaluate $2^{-3}$ | $\dfrac{1}{2^{3}} = \dfrac{1}{8}$ |
| Evaluate $5^{-1}$ | $\dfrac{1}{5^{1}} = \dfrac{1}{5}$ |
Proofs of Laws of Exponents – Practice
Laws of Exponents
| Law | Expression | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Product of Powers | $a^{m} \times a^{n}$ | $a^{m+n}$ |
| Quotient of Powers | $\dfrac{a^{m}}{a^{n}}$ | $a^{m-n}$ |
| Power of a Power | $(a^{m})^{n}$ | $a^{mn}$ |
| Zero Exponent | $a^{0}$ | $1$ |
| Negative Exponent | $a^{-n}$ | $\dfrac{1}{a^{n}}$ |
Refer to the table for a recap, and practice applying the laws of exponents.
Proofs of Laws of Exponents – Summary
Key Learnings from this Text:
- Understanding and proving the laws of exponents solidifies the foundation in algebra and higher-level mathematics.
- Each law, whether it's the Product of Powers or Quotient of Powers, simplifies complex exponential expressions.
- Applying these rules to variables and numerical bases demonstrates their universal applicability.
- The proofs of these laws lie in their ability to systematically expand and simplify exponential expressions.
Proofs of Laws of Exponents – Frequently Asked Questions
Transcript Proofs of Laws of Exponents
Snipe has arrived at the fabled Mushroom Castle, and uses the lost pieces to pass through the Door of Wisdom. But this is ridiculous: how can he possibly squeeze through that tiny door? Oh, hello! It looks like the frog wants Snipe to drink a magic potion! But is this frog trying to make Snipe croak? In order to confirm that this frog isn't slimy, Snipe will have to explore the laws of exponents. The potion is inscribed with a mathematical expression 'x' to the 'a' times 'x' to the 'b'. Over the door there's another expression 'x' to the quantity 'a' plus 'b'. If these expressions are the same, the potion will squeeze Snipe through the door. How would YOU confirm the equivalence of these two expressions? One option is to substitute values for the variables, and see if the equation holds true. That won't PROVE that the equation is true for ALL values, but experiments with SOME sets of values will give Snipe more confidence. So, let's select a few values at random: 'x' equals 3, 'a' equals 2, and 'b' equals 4. Now we plug in our values for the variables. On the left, we have 3 squared times 3 to the 4th. Three squared is 9, and 3 to the 4th is 81. Nine times 81 is seven twenty-nine. On the right we have 3 to the quantity 2 plus 4. That's 3 to the 6th. Three to the 6th is seven twenty-nine as well! The results were the same! Based on this one experiment, would you drink the potion, or would you try more values? Snipe decides to check four more sets of values, and the equation holds for each set! He still can't be COMPLETELY sure that it's true for all values, but he's more certain than before. Snipe trusts the frog and guzzles the potion, and it works! What's going on here? Are those dragonflies? The frog points to a dragonfly which has an expression on it: 'x' to the 'a', raised to the power of 'b'. Snipe looks up at the door, which has the expression 'x' to the 'a' 'b' floating above it. Is it wise to trust the frog and fly the friendly flies? How can Snipe prove these expressions are equivalent? Substituting values worked before, but this time he wants something more certain. Snipe can use what he knows about exponents to manipulate one or both expressions until it's clear that they are equal. This won't be a formal proof, but it will be an effective argument that is much more certain than just experimenting with specific values. He starts by simplifying the challenge, and assumes that 'a' and 'b' are positive integers. X' to the 'a' means 'x' multiplied together a total of 'a' times. Raising to the power of 'b' means that we have 'x' to the 'a' a total of 'b' times. How many times is 'x' multiplied by itself altogether? That's 'a' plus 'a' plus 'a' and so on, 'b' times, which is that same as 'a' times 'b'! That means the expression equals 'x' to the 'a' 'b'! By manipulating one side of the equation, we've shown that 'x' to the 'a', raised to the power of b, is the same as 'x' to the 'a' 'b', at least when the exponents are positive integers. But Snipe still needs to establish the equation for the cases when one or both exponents ARE negative. And he'd like to formally PROVE it, justifying each step with the rules of arithmetic that he already knows. Let's first look at the case where 'a' is negative and 'b' is positive. Before we start with the equation, let's define 'a' as negative 'c.' Using substitution, we can plug in negative 'c' in for 'a', giving us 'x' to the negative 'c', to the 'b'. Using the definition of a negative exponent, 'x' to the negative 'c' is 1 over 'x' to the 'c'. The power of a quotient law allows us to apply the exponent 'b' to the numerator and denominator: 1 to the 'b', over the quantity 'x' to the 'c' raised to the 'b'. 1 to any power is still 1, so 1 to the 'b' is equal to 1. Since 'c' and 'b' are both positive, we can use what we proved before to write 1 over 'x' to the 'c' 'b'. Again using the definition of a negative exponent, 1 over 'x' to the 'c' 'b' is equal to 'x' to the negative 'c' 'b' The associative property of multiplication allows us to write negative 'c' times 'b' as negative 'c', times 'b' And finally, using substitution of 'a' equals negative 'c' gives us 'x' to the 'a' 'b'. That's what we wanted to prove! Snipe has now written a formal proof of the power of a power rule when only 'a' is negative. He quickly does the same for the other cases and now knows that the rule holds for all values of 'a' and 'b'. Snipe confidently takes off and buzzes through the distant door! Snipe finds himself in front of a locked trapdoor, and here's that slippery frog again, offering a key. While Snipe sizes up this amphibian offer, let's review our exploration of the laws of exponents. We established the truth of equations in three different ways. First, we substituted values for the variables. This gets the job done quickly, and is easy to understand, but this method doesn't provide certainty for ALL values of the variables. Then, we made a strong argument by manipulating one side of the equation. This was persuasive, but we didn't give mathematical RULES to justify every step. Our last effort was a formal PROOF, where every step was justified with a mathematical RULE. Formal proof is often the most challenging way to establish mathematical truth, but it's also the most convincing. Snipe decides to blindly trust the frog and puts the key into the lock. Oh, a frog princess...how, um, beautiful! So what happens now, a kiss? Aack!
Proofs of Laws of Exponents exercise
-
What is the meaning of the key words?
HintsAn example of the product:
the product of $4\times5 = 20$.
An example of the quotient:
the quotient of $\frac{20}{4} = 5$.
A fraction has a numerator and a denominator.
Solution- The value above the line of a fraction $=$ Numerator.
- The value below the line of a fraction $=$ Denominator.
- A result obtained by dividing one quantity by another $=$ Quotient.
- The result of multiplying two or more numbers together $=$ Product.
-
Use the product rule for indices
HintsThe product rule for indices says that if the base is the same, we add the powers.
For example, $2^3\times2^4 = 2^{3+4} = 2^7$
When adding powers remember that anything to the power $1$ does not have a power written.
For example, $6 = 6^1$, $3 = 3^1$
Solution- $4^3\times4^2 = 4^{2+3} = 4^5$
- $4^2\times4^2 = 4^{2+2} = 4^4$
- $4^5\times4^2 = 4^{5+2} = 4^7$
- $4\times4^2 = 4^{1+2} = 4^3$
-
Identify the laws of Indices.
HintsAn example of the product of powers rule is, $x^4 \times x^3 = x^7$.
We add the powers when the base is the same.
An example of the quotient of powers rule is, $x^8 \div x^3 = x^5$.
We subtract the powers when the base is the same.
An example of the power of powers rule is, $(x^4)^6 = x^{24}$.
We could write this as, $x^4 \times x^4 \times x^4 \times x^4 \times x^4 \times x^4$.
In short, multiply the powers $x^{4\times6} = x^{24}$.
There are $4$ correct answers here.
SolutionThere are $4$ correct answers:
- $x^{a} \times x^{b} = x^{a+b}$
- $x^{a} \div x^{b} = x^{a-b}$
- $(x^{a})^{b} = x^{ab}$
- $y^{c} \times y^{d} = y^{c+d}$
-
Manipulate the indices.
Hints- We start this by stating that $a$ and $b$ are greater than $0$.
- Next, we are manipulating the left side to look like the right side.
- We expand the $y$'s to the power of $a$ for the next line.
- We then show there are $b$ lots of $y^a$.
- Finally, we show this shortens to the right side.
SolutionHere we can see the steps in the correct order.
-
Use the power of powers rule.
HintsWe use the power of power rule.
Multiply the indices if the base is the same.
For example, $(x^5)^3 = x^{5\times3} = x^{15}$.
To show this rule we could write this out in full and use the product of powers rule.
For example,
$(x^5)^3 = x^{5} \times x^{5} \times x^{5} = x^{5+5+5} = x^{15}$
Solution$(x^2)^4 = x^{2} \times x^{2} \times x^{2} \times x^{2} = x^{2+2+2+2} = x^{8}$.
In short, $x^{2\times4}$ $ = x^8$.
-
Prove the power of powers law.
HintsWe use all the laws of indices for this proof. Here is one example.
Another example of the laws used.
There are $3$ laws used in this proof, therefore $3$ correct answers.
SolutionThis is the complete proof with the $3$ laws used.
- Law of Negative Indices.
- Power of a Quotient Law.
- Power of Powers Law.