Writing Linear Equations

Basics on the topic Writing Linear Equations
If you only know a couple points on a line, how can you write a linear equation into slope-intercept form, y = mx + b?
A couple points on a line is all you need. To calculate the slope, decide which of two points will be the first ordered pair and the second, and then plug the x and y-values into the slope formula. Alternatively, you may be able to look at the graph and determine the rise over the run between any two points – the change in the height divided by the change in the width.
After you have figured out the slope, the m-value in the slope-intercept form, you can figure out the b-value, the y-intercept. Into the slope intercept form you have written so far, use the coordinates for one point on the line and plug in those values for x and y.
To calculate the y-intercept, isolate the b-value. There are some other shortcuts to help you write linear equations. If lines are parallel, they have the same slope but different y-intercepts. If the lines are perpendicular, the slopes will have a negative inverse (negative reciprocal) relationship, and the products of the two slopes will be -1. This is sort of hard to describe using words. Maybe you had better watch this video on the topic of writing linear equations.
Write equations of the line.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GPE.B.5
Transcript Writing Linear Equations
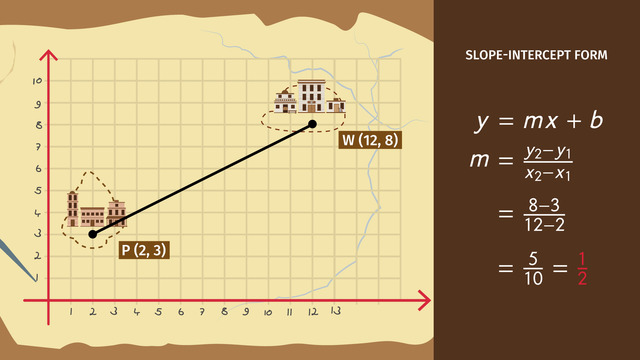
Back in the day when the west was still a frontier, W.J. Palmer was in his office planning to build a railroad track between two cities. He wanted to make the track a straight line so that it'd be the shortest route possible. To figure out how to do so, he uses linear equations. Let's take a look at the map. We can turn it into a coordinate system.
We know the coordinates of the two ciities that will be connected by the train tracks. Palm Valley is at point P (2, 3) and Wildwood Crest is at point W (12, 8). Because the track will be a straight line between the two points, we can write a linear equation to represent this line. In order to write the equation in slope-intercept form, y = mx +b, we need to find the slope, m, and the y-interecept, b.
Calculate slope
To calculate slope, we'll use the formula m= y2 minus y1 over x2 minus x1. So let's plug in our points. We'll call point (2, 3) (x1, y1) and point (12, 8) (x2, y2). When plugged into the formula, we get 8 minus 3 over 12 minus 2... , ...which is 5 over 10. This reduces to 1/2, so the slope is 1/2. Now that we have m, we can put that into our formula.
We also need to choose a point to plug in for x and y. Let's use the coordinates of Palm Valley, (2, 3). Now we have 3 equals 1/2 times 2 plus b. 1/2 times 2 is 1. To find b, you need to subtract 1 from both sides of the equals sign. B equals 2. Now that you know m is 1/2 and b is 2, you know the equation of this line is y= 1/2 x + 2 W. J. Palmer's plans are looking great.
New track
But suddenly he realizes that the railroad will go through a forest that's home to the famous gold rush bugs. Since W.J. Palmer is a big bug enthusiast, he wants to save the bugs and decides to make a Plan B. Palmer decides to start from a different point in Palm Valley. The point is (2, 4). Palmer also wants this track to be parallel to his original track. Let's write the equation for the line of the new track.
Parallel lines have the same slope, so we can keep m equal to 1/2 again. Let's use our slope-intercept formula again and plug in (2, 4) to find our y-intercept, b, for the new route. So we have 4 equals 1/2 times 2 plus b. 1/2 times 2 is 1. So 4 equals 1 plus b. Subtract 1 from both sides. B equals 3.
If we plug in m and b, the new equation is y = 1/2 x + 3. The new railroad track is built and everything looks great! But W. J. Palmer found out that his little bug friends have to cross the tracks to get to their favorite field of flowers. Many bugs have died on their way across the tracks. So Palmer decides to build a bridge perpendicular to the tracks so that the bugs can cross the tracks safely.
Find the equation
The bugs are located in the forest at point B (6, 5). In order to build the bridge, we need to find the equation of the line that is perpendicular to the track and goes through (6, 5). There are two ways to find the slope of a perpendicular line. The first way is to make sure that the product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines equals -1.
The perpendicular line
We know the first slope is 1/2. So if we plug in 1/2 for m1, we can solve for m2 by multiplying both sides by 2. -1 multiplied by 1/2 is -2 -1 divided by 1/2 is -2. The second way to find the slope of a perpendicular line is to remember that perpendicular slopes are negative reciprocals of each other. Negative means that we will need to multiply by -1. Reciprocal means that we will flip the numerator and denominator. -2 over 1 simplifies to -2.
So we got the slope of the line that's perpendicular to the track, but we still need to find b. If we use slope-intercept form again, y = mx +b, we'll plug in -2 for m and use the point (6, 5) for x and y. So the equation will be 5 = -2 times 6 plus b -2 times 6 is -12. Since we have a negative 12, we will need to add 12 to both sides.
5 plus 12 is 17, so b is 17. If we plug in the values for m and b, the equation for the bridge is y = -2 x + 17. And this, my children, was the story of W. J. Palmer--a true friend to all beings on 6 legs.
Writing Linear Equations exercise
-
Determine the linear equation in slope-intercept form.
HintsThe slope-intercept form is: $y=mx+b$.
- $m$ is the slope
- $b$ is the y-intercept
To calculate the y-intercept, you have to plug in one of the given points.
When calculating the slope, make sure to be consistent when ordering the points.
SolutionA linear equation written in slope-intercept form is: $y=mx+b$.
$m$ represents the slope, and $b$ represents the y-intercept.
In order to identify the linear equation, we start with the slope, which is given as the change in y divided by the change in x:
- $m=\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}$
- $m=\frac{8-3}{12-2}=\frac{5}{10}=\frac{5\div 5}{10\div 5}=\frac12$
- $y=\frac12x+b$
$\begin{align*} 3&=\frac12\times2+b\\ &=1+b \end{align*}$
Subtracting $1$ leads to $b=2$.
As a result we get the linear equation in slope-intercept form:
- $y=\frac12x+2$
- $8=\frac12\times 12+2=6+2$ $\surd$
-
Explain how to set up an equation for a parallel line.
HintsParallel lines always have the same slope.
A linear equation in slope-intercept form is: $y=mx+b$.
- $m$ is the slope
- $b$ is the y-intercept
You can calculate the y-intercept.
To figure out the y-intercept, plug the coordinates of the given point into the linear equation. This will result in a value for $b$.
SolutionRemember, the slope-intercept form is: $y=mx+b$.
$m$ is the slope, and $b$ is the y-intercept. Two parallel lines have the same slope.
- $m=\frac12$
- $y=\frac12x+b$
- $4=\frac12\times 2+b=1+b$
- $b=3$
- $y=\frac12x+3$
-
Find the equation of the line that is perpendicular to $y=\frac12 x+2$ and passes through $B(7,5)$.
HintsIn order to write the linear equation in slope-intercept form, you have to determine the slope and then calculate the y-intercept.
$y=m_1x+b_1$ and $y=m_2x+b_2$ are two linear equations.
The lines are perpendicular if $m_1\times m_2=-1$.
In order to find the y-intercept, you have to plug the coordinates of a given point into the equation $y=mx+b$.
SolutionA linear equation in slope-intercept form is:$y=mx+b$.
The equation of the purple line has to be perpendicular to $y=\frac12x+2$.
So, $\frac12\times m=-1$.
Multiplying by $2$ results in $m=-2$.
Now, we can write the equation $y=-2x+b$.
We still have to determine the y-intercept, so we plug the coordinates of $B(7,5)$ into the equation and solve for $b$:
$\begin{array}{rcl} 5&=&-~~2\times 7+b\\ 5&=&-14+b\\ \color{#669900}{+14}&&\color{#669900}{+14}\\ 19&=&~~~~~b \end{array}$
Finally, we know the equation of the purple line which is perpendicular to the orange line:
$y=-2x+19$
-
Decide which equations are represented by the given graphs.
HintsKeep in mind:
- increasing lines have a positive slope
- decreasing lines have a negative slope
Remember - rise over run.
"Rise" means the line goes upwards or downwards while "run" means the line goes to the right.
You can look at the graphs to find the y-intercepts.
Which part of the equation represents the y-intercept?
SolutionEach equation is written in slope-intercept form: $y=mx+b$.
- $m$ is the slope
- $b$ is the y-intercept
Green line
- y-intercept is $2$
- rise: $1$ (up), run: $2$, so $m=\frac 12$
- So the equation is $y=\frac12x+2$
- y-intercept is $0$
- rise: $2$ (up), run: $1$, so $m=\frac 21=2$
- So the equation is $y=2x$
- y-intercept is $2$
- rise: $1$ (up), run: $3$, so $m=\frac 13$
- So the equation is $y=\frac13x+2$
- y-intercept is $3$
- rise: $1$ (up), run: $4$, so $m=\frac 14$
- So the equation is $y=\frac14x+3$
-
Identify the lines that are parallel or perpendicular to the orange line.
HintsParallel lines have the same slope.
Perpendicular lines meet at a right angle.
At least one line is neither parallel nor perpendicular to the orange line.
SolutionLet's consider the orange line: $y=\frac12x+2$.
You can identify the slope by calculating rise over run of the line. Count the units you go up or down and divide this number by the number of units you go to the right. The slope is positive if the line is increasing, or rises to the right.
Parallel lines have the same slope, so the green line is parallel to the red line. Both lines have the slope $m=\frac12$.
Perpendicular lines meet at a right angle, and the two slopes are always the negative reciprocals of one another, which means the product of the two slopes is always $-1$. The blue line is perpendicular to the red line. It has a slope of $m=-2$.
$m_1 \times m_2=\frac12 \times -2 = -1$
-
Write the equations for the given graphs in different forms.
HintsSimplify the slope as much as possible:
$\frac22=1$
- slope-intercept form: $y=mx+b$
- point-slope-form: $y-y_1=m(x-x_1)$
- standard form: $Ax+By=C$
- $m$ is the slope
- $b$ is the y-intercept
- $P(x_1,y_1)$ is a point on the line
For standard form, you have to look at both the x- and y-intercepts: $(0,5)$ and $(7,0)$.
SolutionFind the solution on the right side.
Green line
We're looking for the equation in slope-intercept form, $y=mx+b$.
- the y-intercept is $1$
- the slope is given by the change in height divided by the change in width, $m=\frac11=1$
Violet line
We're looking for the equation in point-slope form, $y-y_1=m(x-x_1)$.
- $x_1=0$ is given as part of the equation, so we use the y-coordinate $y_1=4$
- the slope is given by the change in height divided by the change in width, $m=\frac18$
Orange line
We're looking for the standard form, $Ax+By=C$.
- $B=7$ is already given
- the y-intercept is $(0,5)$
- plugging $x=0$ and $y=7$ into the equation, we get $7\times 5=C$, so $C=35$
- the x-intercept is $(7,0)$
- plugging $x=7$ and $y=0$ into the equation, we get $A\times 7=35$, dividing by $7$ gives us $A=5$













Funny and informative! It's great! Keep up the good work!