Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiplies of 10
- Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Explanation
- Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Strategies
- Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Distributive Property Method
- Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Steps
- Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions about Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10
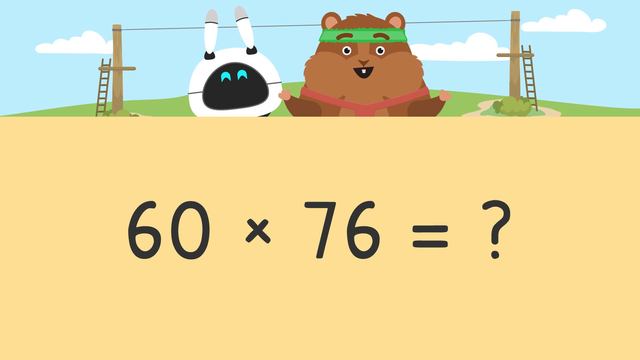

Basics on the topic Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiplies of 10
Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Explanation
In this text, we will learn how to multiply 2-digit numbers by a multiple of 10. This skill will help us solve multiplication problems quickly and efficiently. We will explore different strategies and examples to understand this concept better.
When we multiply a number by a multiple of 10, the product will always have the same digits as the original number, but with one or more zeros written at the end. You might wonder why exactly this pattern occurs. This happens because multiplying by 10 means increasing the value of the number by ten times.
For example, if we multiply 25 by 10, the product will be 250. We can see that the digits 2 and 5 remain the same, but there is a zero at the end and the value of each digit has become 10 times more.
Let's look at another example. If we multiply 36 by 100, the product will be 3,600. Again, the digits 3 and 6 remain the same, but there are two zero at the end and the value of each digit has become 100 times more.
Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Strategies
There are a few strategies we can use to multiply 2-digit numbers by a multiple of 10:
- Using Mental Math: If the multiple of 10 is a single-digit number, we can simply write the appropriate number of zeros at the end of the original number.
For example, to multiply 45 by 10, we write a zero at the end to get 450. This strategy is very helpful when multiplying by 10, 100, and 1000 but less helpful when multiplying by their multiples, such as 20, 300, 5000.
- Using Place Value: We can also use place value to multiply. We multiply the digit in the ones place of the original number by the multiple of 10. Then, we multiply the digit in the tens place by the multiple of 10 and write an additional zero. Finally, we add the two products together.
For example, to multiply 34 by 10, we multiply 4 by 10 to get 40, and multiply 30 by 10 to get 300. Then, we see that the values of each digit increased ten times, and we have a placeholder of 0 in the ones place
- Using the Distributive Property: Another strategy is to use the distributive property. We can break down the original number into its place value parts and multiply each part by the multiple of 10. Then, we add the products together.
For example, to multiply 27 by 50, we can break down 27 into 20 + 7. We multiply 20 by 50 to get 1,000, and multiply 7 by 50 to get 350. Finally, we add 1,000 and 350 to get 1,350.
Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Distributive Property Method
In exploring the concept of multiplication using the distributive property, an area model serves as an effective visual aid. In this approach, we decompose the factors into tens and ones, or their expanded form, and use these numbers to define the dimensions of a rectangle. The product of the multiplication is then represented by the total area of this rectangle.
Consider the example where we multiply fifteen (15) by seventy (70). First, we break down fifteen into its expanded form: ten (10) plus five (5). These values represent the sum of the lengths of the rectangle's sides. Next, we place seventy (70) as the width of the rectangle. Inside the rectangle, we apply multiplication for each part: 70 × 10. 70×10 gives us 700, and 70 × 5. 70×5 results in 350. By summing these areas – 700 and 350 – we find the total area, 1050, which is the product of our original equation.
Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Steps
In this example, we are going to show all the steps in detail of the multiplication process.
Let's explore the multiplication of 20 and 15 using distributive property and present it in an area model.
First, we position the number twenty (20) along the left side of the area model, as this is our multiple of 10.
Then, we decompose the number fifteen into its expanded form, which is ten plus five (10 + 5). This expanded form is placed along the top of the area model.
In the area model, our first task is to multiply twenty by ten (20 × 10). In this step, we focus on the values of the numbers, disregarding the zeros temporarily. Multiplying two (from 20) by one (from 10) gives us two. Since the original numbers were ten times greater each, we need to increase the product (2) by 100. Thus, the product of twenty times ten is two hundred (20 × 10 = 200).
Next, we move to multiplying twenty by five (20 × 5). Here, we multiply the natural numbers first: two times five, which equals ten. In this instance, one of the original numbers was 10 times greater, so we will need to make sure to increase the value of the product by 10 too. Therefore, the product of twenty times five is one hundred (20 × 5 = 100).
Finally, we add the sub-products 200 and 100 and arrive at the final product 300.
Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10 – Summary
- Multiplying 2-digit numbers by a multiple of 10 is a useful skill that allows us to solve multiplication problems quickly.
- We can use strategies like mental math, place value, and the distributive property to find the product.
- Remember, when we multiply by a multiple of 10, the digits of the original number remain the same, additional zeros appear at the end of them and the new digits have a value 10 or 100 times the original.
- When using the distributive property method, follow the steps:
| Step # | What to do |
|---|---|
| 1 | Set up an area model with a multiple of 10 on the left side. |
| 2 | Rewrite the two-digit number in expanded form – write the expression on the top of the area model. |
| 3 | Multiply the natural numbers first – natural numbers are all counting numbers starting with one. |
| 4 | Add the products – add the newly calculated products to find the overall product. |
Frequently Asked Questions about Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiples of 10
Transcript Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiplies of 10
“Imani, Check this out!” “That looks AMAZING!” “ We can build a zipline course right HERE!” “ I need to calculate how much of the materials I'm going to need to build it.” By “Multiplying Two-Digit Numbers by Multiples of Ten", (...) we can figure out how much of the materials Mr. Squeaks will use to build his zipline. When multiplying single-digit whole numbers by ten, we can simply add a zero to the end of the number. This means that the digit's value becomes ten times greater. When multiplying larger numbers, we can use what we know about multiples of ten and area models to make our computation easier. Mr. Squeaks needs wood posts. The posts came in bundles of fifteen and he will use twenty bundles. Let’s set up the equation twenty times fifteen... and make an area model. Put the twenty on the left side of the area model. Now, look at the number fifteen. Since we know we can use mental math when multiplying by multiples of ten... let’s rewrite this number in expanded form. Fifteen is the same as saying ten plus five. Write this expression on top of the area model. To multiply, (...) first start with twenty times ten. Start by multiplying the digits that are natural numbers. Remember, natural numbers are all counting numbers starting with one, so we are not looking at the zeros. Two and one are natural numbers, (...) so two times one equals two. Now, look at the total number of zeros in the problem. There are two zeros, so we add two zeros to the product to show that it is one hundred times greater. Next, we look at twenty times five. Again, multiply the natural numbers first. Two times five equals ten. There is one zero in this equation. We will add that to the product to show that it is ten times greater. Add the partial products together… Two hundred plus one hundred equals three hundred. Mr. Squeaks will use three hundred posts to build his zip line course! Next, he needs thirty bundles of sixty-three-inch rope. To figure out how much rope he will use, we’ll multiply thirty and sixty-three. Set up the area model and put the thirty on the lefthand side. To make sixty-three easier to multiply, we will write it in expanded form. What is the expanded form of sixty-three? Sixty plus three. Start by multiplying the natural numbers in the equation... three times six. Three times six equals eighteen. Look at the number of zeros in the equation. How many zeros do we add to the product? We add two zeros,(...) thirty times sixty is eighteen hundred. Now, multiply thirty times three. What do we multiply first? Three times three (...) which equals nine. How many zeros do we add to the product? We add one zero. What do we get when we add the partial products? One thousand eight hundred, ninety. The zipline course will use one thousand eight hundred, ninety inches of rope. Lastly, Mr. Squeaks needs cable wire. He will use sixty bundles that have seventy-six inches of wire each. Pause the video and try this one on your own before we review it. How many inches of cable wire will Mr. Squeaks use? He will use four thousand, five hundred sixty inches of cable wire. Let’s check over the steps. First, set up the area model with sixty on the left side... and seventy-six is rewritten as seventy-plus six. Inside the model, multiply six times seven is forty-two… now add the two zeros to the product. Repeat that step in the other grid… six times six equals thirty-six. Add a zero to show the product is ten times greater. Finally, add the partial products. Four thousand five hundred sixty inches of cable wire. Remember, (...) We can multiply two-digit numbers by multiples of ten by... setting up an area model with the multiple of ten on the left side. Rewriting the two-digit number in expanded form on the top. Inside the boxes, first, multiply the sets of natural numbers ... and then add zeros to the products based on the number of zeros in the problem. Finally, add the partial products. “ TA-DA!” “ LET’S CHECK IT OUT!” [ squealing with excitement as it “rides” the zipline] “Beep! Boop! Bop!” “This IS AMAZ…..”[starts to speed up and sees he's heading right for the computer screen] [Mr. Squeaks is waving his arms and warning to get out of his way. He’s coming through.] “WOOOOOAH (...) LOOK OUUUUUT!”
Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiplies of 10 exercise
-
How would you write the number 24 in expanded form?
HintsThe 2 is in the tens place, so how many zeros are there?
The 4 is in the ones place. Are there any zeros in the ones place?
Solution- There are 2 tens, and 2 tens are 20.
- There are 4 ones, and 4 ones are 4.
-
Which image represents the correct area model?
HintsRemember to set up your model with number that is a multiple of 10 on the left side.
Write the second number in expanded form.
SolutionMultiply 20 and 32:
- Put 20 on the left-hand side
- Write 32 in expanded form
- Multiply the natural numbers
-
Calculate how much rope Mr. Squeaks will use.
HintsRemember to put the number that is a multiple of 10 on the left side of the area table
Next, write 42 in expanded form and set up your equations.
SolutionMultiply 20 and 42
- Put 20 on the left-hand side
- Write 42 in expanded form
- Multiply the natural numbers
- Then add the number of zeros in the equation
- Finally add the partial products
-
Determine how much cable wire is needed.
HintsCreate an area table to show 50 x 36.
Find:
- 50 x 30
- 50 x 6
SolutionMultiply 50 and 36:
- Put 50 on the left-hand side
- Write 36 in expanded form
- Multiply the natural numbers
- Then add the number of zeros in the equation
- Finally add the partial products
-
What is your first step to setting up the area model?
HintsWhat number do you put on the left side?
After drawing a rectangle, this shows the first step.
Solution*Once you have your equation of 30 x 45, then put 30 on the left-hand side of the area model.
-
Determine how much material is needed.
HintsYou will set up two area tables, one for small jackets and one for large jackets.
First, multiply 30 x 22 for the small jackets
SolutionFor small jackets:
- Multiply 30 and 22
- Put 30 on the left-hand side
- Write 22 in expanded form
- Multiply the natural numbers
- Then add the number of zeros in the equation
- Finally add the partial products
- Multiply 40 and 45
- Put 40 on the left-hand side
- Write 45 in expanded form
- Multiply the natural numbers
- Then add the number of zeros in the equation
- Finally add the partial products
Multiplying up to Three Digits Using the Standard Algorithm
Multiplying up to Three Digits Using the Standard Algorithm—Let's Practice!

Multiplying Two-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
Multiplying Two-digit Numbers by Two-digit Numbers — Let's Practice!
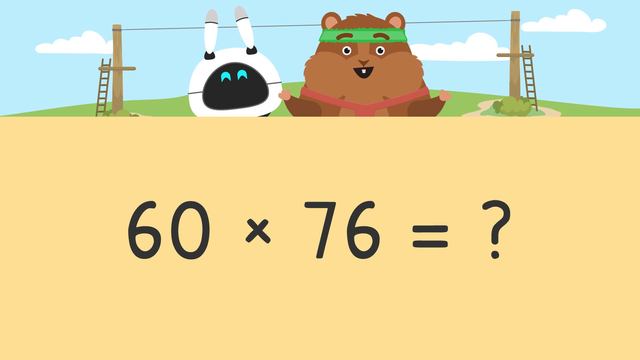
Multiplying 2-Digit Numbers by Multiplies of 10

Multiplying Tens, Hundreds and Thousands
Multiplying Two-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers Using an Area Model
Multiplying Two-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers Using an Area Model—Let's Practice














