Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle
- Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle – Definition
- Angle Sum Theorem
- Finding Missing Angles using the Angle Sum Theorem

Basics on the topic Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle
Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle – Definition
Every triangle you see, whether it's a sign, part of a bridge, or a piece of art, embodies a fascinating aspect of geometry through its interior and exterior angles. These angles aren't just numbers; they are fundamental to understanding the triangle's shape and how it relates to the space around it. In the world of triangles, the angles inside (interior) and those formed by extending a side (exterior) play crucial roles in geometry, influencing everything from architectural designs to the essence of artistic compositions.
The interior angles of a triangle are the angles inside the triangle's corners. The exterior angles are formed by extending one side of the triangle and measuring the angle outside the triangle adjacent to an interior angle.
Angle Sum Theorem
The Angle Sum Theorem (also known as the Triangle Sum Theorem) tells us that no matter what type of triangle we have, the three interior angles always add up to 180 degrees.
Let’s take a look at some problems to solve by applying the Angle Sum Theorem.
Is it possible to have a triangle with angle measurements of $45^\circ$, $15^\circ$, and $40^\circ$?
- Find the sum of the given angles, $45 + 15 + 40 = 100$.
- The angle sum does not equal exactly $180$ degrees, and therefore these angle measurements are impossible for a triangle.
Is it possible to have a triangle with angle measurements of $55^\circ$, $20^\circ$, and $105^\circ$?
- Find the sum of the given angles, $55 + 20 + 105 = 180$.
- The angle sum is equal to exactly $180$ degrees, so, therefore these angle measurements are possible for a triangle.
Go ahead and apply the Angle Sum Theorem in different scenarios:
Is it possible to have a triangle with angle measurements of $60^\circ$, $60^\circ$, and $60^\circ$?
Finding Missing Angles using the Angle Sum Theorem
Now that you understand that the angle sum theorem states that a triangle’s angles must have a sum of exactly $180$ degrees, let’s apply this knowledge to find missing angles, without needing to use a protractor.
What is the measurement of the missing angle?
- 1️⃣ The sum of the interior angles must equal exactly $180^\circ$, and since we are missing one angle measurement, this value can be represented with a variable, $x$.
- 2️⃣ The equation $55 + 70 + x = 180$ can be used to represent the interior angles of this triangle.
- 3️⃣ Solve the $x$ to find the missing angle.
$55+70+x=180$
$125+x=180$
$x=55$
Try it yourself:
Exterior Angle Theorem
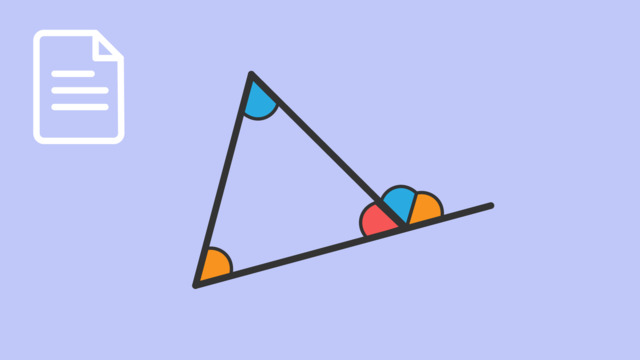
The Exterior Angle Theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles (also referred to as opposite interior angles).
Think of the Exterior Angle Theorem as opening a door slightly. That opening is the exterior angle of a triangle, similar to the part of the door still closed, which represents the two non-adjacent interior angles. Essentially, the open part (exterior angle) matches the closed part's width (sum of the two interior angles). It shows that the exterior angle fills in the space the other angles don't, making sure all angles at that vertex add up to a straight line or $180$ degrees.
Applying the Exterior Angle Theorem
Let's explore how the Exterior Angle Theorem works with a few examples.
If one interior angle of a triangle is $60^\circ$ and another is $70^\circ$, what is the measure of the exterior angle adjacent to these angles?
- 1️⃣ First, find the sum of the interior angles: $60 + 70 = 130^\circ$.
- 2️⃣ According to the Exterior Angle Theorem, the exterior angle is equal to the sum of these two interior angles, so the exterior angle is $130^\circ$.
If a triangle has interior angles of $50^\circ$ and $60^\circ$, what is the measure of the exterior angle next to these angles?
- 1️⃣ Add the interior angles: $52 + 58 = 110^\circ$.
- 2️⃣ The exterior angle will be $110^\circ$, as it equals the sum of the non-adjacent interior angles.
Go ahead and apply the Exterior Angle Sum Theorem in different scenarios:
Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle – Problem Solving
Use your knowledge of the interior and exterior angles of a triangle to find the missing angle measurements in the problems. Being familiar with finding angles using equations will help solving these problems more easily!
For more practice problem-solving with angles, check out What are Supplementary and Complementary Angles? and Calculations with Supplementary, Complementary, and Vertical Angles to learn more!
Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle – Summary
Key Learnings from this Text:
- The Angle Sum Theorem confirms that every triangle's interior angles sum up to 180 degrees.
- The Exterior Angle Theorem states that an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
- Understanding these principles, including the Angle Sum Theorem and Exterior Angle Theorem, is crucial for solving various geometric problems.
Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle – Frequently Asked Questions
Transcript Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle
Moira is a mosaic master and has just taken on a big space to help the "beautify the city" initiative. She is fascinated by the mosaics of ancient Egypt that are made of colorful tiles, stones, or glass. Moira can easily see how to make a mosaic from Equilateral triangles or isosceles triangles but what about scalene triangles, or any triangle for that matter? To find out, we'll need to explore interior and exterior angles of a triangle. Let's start with a scalene triangle, and extend one side. These angles are known as interior angles because they're on the inside. This angle is called an exterior angle because it is outside of the shape but still shares a side. Exterior angles are adjacent, meaning next to, their respective interior angles. In fact, if we extend all the sides of the triangle we create six exterior angles. But what about these angles? They are outside the triangle, but they're not exterior angles, because they aren't adjacent to interior angles. Each of these angles are called vertical to their opposite interior angles. How do exterior angles relate to their adjacent interior angles? To find out, let's look at one vertex of the triangle and label the angle measures. We'll say this interior angle measures 'x.' So, what is the measure of this opposite angle? It is also 'x' because this angle is a vertical angle to this interior angle. If we say this exterior angle measures 'y', then what is the measurement of this angle opposite of it? It is also 'y' because this angle is vertical to the exterior angle. These four angles actually form a complete circle. Therefore, if we sum x, plus x, plus y, plus y, we get 360 degrees. Simplifying we notice that we get 2x plus 2y equals 360. Actually we could even go further. Do you notice that all the numbers are even? So, we could divide everything by 2. This tells us 'x' plus 'y' is 180 degrees. That means that an exterior angle is always supplementary to its adjacent interior angle. This makes sense, because this is a straight angle. An angle whose rays form a straight line and straight angles always measure 180 degrees. Now, Moira has sketched a triangle with an interior angle of 110 degrees. So, what's the measure of this exterior angle, that we can call 'y'? We know these angles are supplementary, so 110, plus 'y,' is 180 degrees. Isolating the 'y,' tells us that the measure of the exterior angle is 70 degrees. Exterior angles and their adjacent interior angles always sum to 180 degrees, but let's explore other angle relationships in this diagram. From the perspective of this exterior angle, these two angles are called remote interior angles. The remote interior angles are inside the triangle and are the angles far away, also known as remote, from the exterior angle. Let's explore their relationship by first recalling what the sum of all 3 interior angles of a triangle is. The angle sum theorem tells us that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees. Looking at the tile Moira made based on her earlier sketch, we see the 110 degree angle plus these two remote interior angles sum to be 180 degrees. We can see this by breaking off the two remote interior angles and suming them all visually by placing them next to each other. Notice that the two remote interior angles sum to the measure of the exterior angle! We can use this fact that remote interior angles sum to be the mesaure of the exterior angles of a triangle, to solve for unknowns. Suppose we want to find 'x' in THIS diagram. We are given an exterior angle of 100 degrees and two remote interior angles whose measures are 55 degrees, and 'x'. Recall, the exterior angle is the sum of the two remote interior angles so 100 equals 55 plus 'x'. Subtraction gives us 45 degrees for 'x'. These special relationships between exterior angles and interior angles help Moira create her mosaic. But before she unveals her work of art, let's review the angle relationships of interior and exterior angles of a triangle. First, recall what the angles are that you're looking at. The angles on the inside are called Interior angles. The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees. The exterior angle is the angle between any side of a shape, and a line extended from the next side. The sum of an exterior angle and its adjacent interior angle is also 180 degrees. Looking at this exterior angle we can see that the remote interior angles are the two angles inside the triangle that a farther away. The measure of an exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two remote interior angles. So. Now! The moment we've all be waiting for. Moira unveils her effort to beautify the city! I guess Moira was already making the city beautiful by just being herself! Now they are getting a bit more Moira than they bargained for!
Interior and Exterior Angles of a Triangle exercise
-
Define the Angle Sum Theorem.
HintsAll triangles have three interior angles.
Angles $a+b+c=180^\circ$.
SolutionThe sum of the interior angles in a triangle is always equal to $180$ degrees.
-
Apply the Angle Sum Theorem to find the measurement of a missing interior angle of a triangle.
HintsThe Angle Sum Theorem states that the interior angles of a triangle have a sum of 180 degrees.
If you know two of the three angles, you can either
- subtract the known angles from $180$, or
- add the known angles together, and subtract from $180$.
Let's look at an example!
To find $x$, subtract the known angles from $180$.
$180-40-70=70^\circ$
$x=70^\circ$
Solution$a=80^\circ$
Two angles are known $40^\circ$ and $60^\circ$.
Subtract these known values from $180$.
$180-40-60=80^\circ$
-
Apply the Exterior Angle Theorem to find the missing angle.
HintsThe Exterior Angle Theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
The square seen in one angle means that that angle is $90^\circ$, which is also known as a right angle.
The two interior remote angles in this example are $30^\circ$ and $90^\circ$.
SolutionThe missing angle measurement is $120^\circ$.
If the Exterior Angle Theorem is applied, the sum of the two remote interior angles is equal to the exterior angle.
$30+90=120$
-
Apply your understanding of the relationships of interior and exterior angles.
HintsThe Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
The Exterior Angle Theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
Number 3 in this question has two correct equations for the answers.
SolutionThe value of angle $x$ is $\bf{25^\circ}$.
The value of angle $y$ is: $\bf{160^\circ}$.
Angle $z$ can be found by using the equations $\bf{102+z=180}$ or $\bf{44 + 34 = z}$.
-
Identify interior and exterior angles of a triangle with extended sides.
HintsInterior angles are found inside the triangle.
Exterior angles are created when the triangle's legs are extended.
Triangles always have 3 interior angles and they have a sum of 180$^\circ$.
SolutionThe triangle has 3 interior angles as you can see labeled.
Three of the six exterior angles are also labeled.
-
Demonstrate your understanding of interior and exterior triangle angle measurements.
HintsThe Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
The Exterior Angle Theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
To find the measure of angle $a$, notice that the angle adjacent is equal to $105^\circ$. Since angles $a$ and $105^\circ$ are on a straight line, the sum is $180^\circ$.
SolutionMissing Angle Measurements:
- $a=75^\circ$
- $b=105^\circ$
- $c=165^\circ$
- $x=60^\circ$
- $y=15^\circ$
- $z=120^\circ$