Solving Systems of Inequalities by Graphing

Basics on the topic Solving Systems of Inequalities by Graphing
Similar to systems of equations, systems of inequalities are two or more inequalities with the same two variables. To determine the solution to the system, or the point where the inequalities intersect (overlap), a graph is the best method to solve these problems.
First manipulate the inequalities in the system so they are written in slope-intercept form, y = mx + b. This makes it easier for you to create the graph. For each inequality in the system: First put a point on the y-intercept - indicated by the b-value. Next, use the m-value to draw in the slope. To connect the dots, you will use a dotted line to indicate less than or greater than, and a solid line is used for less than and equal to or greater than and equal to situations. Shade the area of the solution set.
This can be tricky – to avoid confusion, it’s a good idea to select a test point. Pop the coordinates of the test point into the inequality. If the inequality is true, shade the area indicated and if false, shade the other side of the line. Follow these steps for each inequality in the system, and the intersection of the shaded areas is the solution that makes all inequalities in the system true.
Solve systems of equations to find solutions to problems.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSA.REI.C.5
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSA.CED.A.3
Transcript Solving Systems of Inequalities by Graphing
Frank, the insurance man, is on a flight to Peru to track down Adventure Mike in the Peruvian jungle. Adventure Mike needs to renew his Ultra Danger Insurance Package. Otherwise, he will not have any insurance on his various adventures.
The system of linear inequalities
Frank takes out his phone to look at the text message that he received a few days ago from Adventure Mike. The text message provides a hint as to which region in the jungle Adventure Mike is searching for ancient relics. Frank knows that Adventure Mike likes to communicate in riddles. He recognizes Mike's missive as a system of linear inequalities.
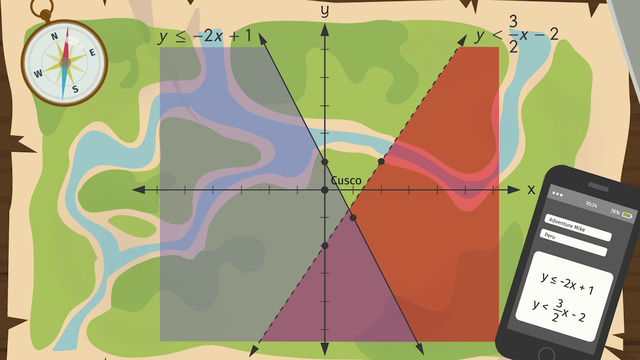
Good thing Frank knows how to solve a system of linear inequalities by graphing. Let's see how Frank solves the system of linear inequalities. Here's a map of the surrounding region. Since we have a system of linear inequalities, we need to include the x- and y-axes in order to graph them. Our starting point, or the origin, is the city of Cuzco.
We need to graph the system of inequalities. Each inequality is written in slope-intercept form. For the first inequality, 1 is the y-intercept or the ordered pair (0, 1). To find the second point, we use the slope of the line. The slope of the line is -2 or -2 over 1. We move down 2 from the y-intercept and right 1. The resulting ordered pair is (1, -1).
Less than or Equal to
Since the inequality represents 'Less than or Equal to', the graph of the inequality is a solid line. All of the points to the left of the inequality are true. We can shade to the left of the inequality line. For the second inequality, 2 is the y-intercept, or the ordered pair (0, -2). To find the second point, we use the slope of the line.
Less than
The slope of the line is 3 over 2. We move up 3 from the y-intercept and right 2. The resulting ordered pair is (2, 1). Since the inequality represents 'Less than', the graph of the inequality is a dotted line. Since all of the points to the right of the inequality are true. We can shade to the right of the inequality line.
The solution to the system of inequalities is where the shading from each inequality overlaps. Frank knows in which part of the jungle to look, so he sets off to find Adventure Mike. Wow! Frank finds an ancient Incan temple. But, what is carved into the side of it? Adventure Mike has left another hint!
Frank pulls out his map again so he can crack this clue and narrow down the possible whereabouts of Adventure Mike. We need to graph the inequality. The inequality is written in slope-intercept form. For the first inequality, -4 is the y-intercept or the ordered pair (0, -4). To find the second point, we use the slope of the line. The slope of the line is 1 over 4. We move up 1 from the y-intercept and right 4. The resulting ordered pair is (4, -3).
Greater than or Equal to
Since the inequality represents 'Greater than or Equal to', the graph of the inequality is a solid line. All of the points above the inequality are true. We can shade above the inequality line. The solution to the system of inequalities is where the shading from each inequality overlaps. Now Frank knows exactly where to go...Oh, so THAT'S why Adventure Mike sent those strange messages in the first place.
Solving Systems of Inequalities by Graphing exercise
-
Explain how to solve a system of linear inequalities by graphing.
HintsKeep in mind
- $\le$ or $\ge$ $\rightarrow$ solid line
- $<$ or $>$ $\rightarrow$ dashed line
Both inequalities are shown in slope-intercept form: $y=mx+b$.
- $m$ is the slope
- $b$ is the y-intercept
To check if the solutions lie above or below the line formed by the graph of the inequality, pick a point and substitute the coordinates into the corresponding inequality.
SolutionWe have the following two inequalities:
- $y\le -2x+1$
- $y<\frac32x-2$
- Draw the y-intercept, $1$.
- Next, draw the slope: move two units down and one unit to the right to find a second point on the line.
- Connect the dots with a solid orange line, because the inequality includes "equal to".
- Shade in the area of the solution set. The solutions lie below the orange line because the inequality includes "less than".
- Draw the y-intercept, $-2$.
- Next, draw the slope: move up three units and two units to the right.
- Connect the dots with a green dashed line, because of the less than sign.
- Shade in the area of the solution set. The solutions lie under the green line.
-
Find all solutions to Adventure Mike's riddle.
Hints$\le$ or $\ge$ inequalities are represented with solid lines while $<$ or $>$ inequalities are represented with dashed lines.
Dont forget:
- $\le$ or $<$ $\rightarrow$ the solutions lie below the line
- $\ge$ or $>$ $\rightarrow$ the solutions lie above the line
For equations written in the slope-intercept form $y=mx+b$, the y-intercept is represented by the term $b$.
SolutionHere you can see the correct graph.
$\mathbf{y\le -2x+1}$
- the orange solid line passes through the y-intercept, $1$
- the solutions lie below the line
- the green dashed line passes through the y-intercept, $-2$
- the solutions lie below the line
- draw solid lines for $\le$ or $\ge$ inequalities
- draw dashed lines for $<$ or $>$ inequalities
- $\le$ or $<$ $\rightarrow$ below the line
- $\ge$ of $>$ $\rightarrow$ above the line
-
Determine where the party will take place.
HintsYou can pick some points and plug them into the inequality to check if they belong to the solution set.
The lines formed by $\le$ or $\ge$ inequalities are part of the solution set.
The lines formed by $<$ or $>$ inequalities aren't part of the solution set.
SolutionLet's start with the inequality $\mathbf{y\ge 2x-2}$:
- The y-intercept is $-2$.
- Move two units up and one unit to the right to plot additional points.
- Connect the points with a solid line, since they are formed by a greater than or equal to inequality. The points on the line are included in our solution set. This inequality is shown by the green line.
- The green shaded area is the solution set for this inequality.
- The y-intercept is $3$.
- Move one unit down and two units to the right to plot additional points.
- Connect the points with a dashed line, since they are formed by a less than inequality. This is shown by the orange line.
- The orange shaded area is the solution set for this inequality.
-
Decide if the location of the treasure lies inside the area where the robbers are searching.
HintsEach point in the coordinate system is given by $P(p_x,p_y)$, where $p_x$ is the x-coordinate, and$p_y$ is the y-coordinate of the point $P$.
Plug each of the given points into all three of the inequalities. The solution must satisfy each of the inequalities.
Pay attention to the $<$ sign in the second inequality.
Are points that are exactly on the line part of the solution set?
Draw the graphs of the inequalities and see if the coordinates are within the intersection area.
SolutionYou can solve a system of three inequalities by graphing in a similar way used for two inequalities:
- Determine the y-intercept
- Use the slope to plot additional points
- Connect the points with a solid or dashed line depending on the inequality sign
- Shade the area belonging to the solution set, either below or above the line, depending on the inequality sign
- The intersection area of all shaded areas is where the hidden treasure can be found
We can use this graph for our decision:
- Crown $(0,3)$ lies on the green and on the red line. But pay attention: the red line is dashed, which means the points on the line aren't included in the solution set. So the robbers can't find this specific treasure.
- Coins $(0,2)$ lie inside the solution area. You can see it directly on the graph.
- Necklace $(2,1.75)$ lies inside the solution area.
- Antique sword $(-1,1)$ lies inside the solution area.
- Bottle of love potion $(2,3)$ lies outside the solution area. When we plug in our y-coordinate, $3$, we see that the inequality is not true: $3\not < \frac14\times 2+3=3.5$
-
Describe how to determine the solution set for the inequality.
HintsAn equation in slope-intercept form is: $y=mx+b$
- $m$ is the slope
- $b$ is the y-intercept
For all $\le$ or $\ge$ inequalities, draw a solid line and for all others, draw a dashed line.
Take any point $P(x_p,y_p)$ and check if $x_p$ and $y_p$ are in the solution set of the given inequality. This helps you verify if the solutions lie above or below the line formed by the inequality.
SolutionHere you can see the graph of $y<\frac32x-2$:
- the y-intercept is $-2$
- for the slope $m=\frac32$, move up three units and right two units
- connect the points $(0,-2)$ and $(2,1)$ with a dashed line
- all solution sets lie below the dashed line
-
Assign the inequality.
HintsThe y-intercept is easily identified in the coordinate system. This is the place where the line crosses the y-axis.
You can calculate the slope by moving up or down and right. For example $m=-\frac34$:
- move three units down (because of the negative sign)
- and move four units to the right
Keep in mind:
- $\ge$ or $\le$ $\rightarrow$ solid line
- $>$ or $<$ $\rightarrow$ dashed line
How do you know if the solution area lies above or below the line formed by the inequality?
- $\ge$ or $>$ $\rightarrow$ above
- $\le$ or $<$ $\rightarrow$ below
SolutionLet's reconstruct the three inequalities:
Start with the red line and the corresponding shaded area:
- The y-interecept is $-3$.
- We move three units up and five units to the right. This gives us the slope $m=\frac35$.
- The line is solid and the shaded area is above the line.
$y\ge\frac35x-3$
$~$
Now let's have a look at the green line:
- The y-interecept is $3$.
- We move up three units and one unit to the right. This gives us the slope $m=3$.
- The line is dashed and the shaded area is below the line.
$y<3x+3$
$~$
Finally, we examine the blue line:
- The y-interecept is $4$.
- We move two units down and one unit to the right. This gives us the slope $m=-2$.
- The line is solid and the shaded area is above the line.
$y<-2x+4$