Solving One-Step Inequalities by Adding or Subtracting

Basics on the topic Solving One-Step Inequalities by Adding or Subtracting
When values are not equal but something else, we use an inequality to solve the problem. If x > 3, we know all the values greater than 3 are in the solution set, but what if the inequality is similar to a one-step equation?
To solve one-step inequalities with a constant added or subtracted to a variable, we follow the same steps as we do when solving similar algebraic equations. To solve, we use the opposite or inverse operation to isolate the variable remembering to keep the inequality balanced. Whatever we do on one side of the inequality sign, we must do on the other side of the sign. Adding and subtracting does not change the direction of the sign, so you can maintain the direction.
It’s a good idea to use a number line when solving inequalities, as it makes solutions easy to visualize and check. Don’t forget, an open dot is for greater than (>) and less than (<) and a closed dot represents inequalities of more than and equal to (≥) and less than and equal to (≤). In the real world, not all things are equal, so understanding inequalities can be very helpful. Watch this video and see what happens to Carol.
Use inequalities to solve problems. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSA.CED.A.3
Transcript Solving One-Step Inequalities by Adding or Subtracting
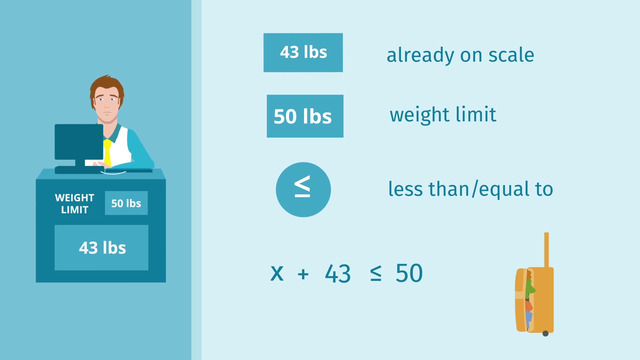
Carol is at the airport checking in for her flight. The airline has a weight limit of 50 lbs for all bags and suitcases combined. Before she puts her last bag on the scale, the scale reads 43 lbs. There's an easy way to find out if she can check her last bag – by solving one-step inequalities with addition and subtraction.
So, let's summarize our given information:
- 43 lbs are already on the scale.
- 50 lbs is the maximum weight limit.
This means her bags should weigh 50 lbs or less. So we use the less than or equal to sign. Now let's use this information to write an inequality.
Writing the Inequality
We want to find out how many pounds Carol can still check. Since this is an unknown value, we will represent it using a variable, for example, x.
We add this to positive 43 lbs for the bags that are already on the scale. All together, this must be less than or equal to 50 lbs.
Solving the Inequality
Now that we have written the inequality, let's solve it. There are a few things to keep in mind when solving inequalities.
- First, remember to use opposite operations to isolate the variable.
- Next, whatever you do to one side of the inequality must be done to the other.
- Lastly, make sure the inequality sign stays the same.
Let's try this problem. Since 43 is added to x, you must use the opposite of addition, subtraction, to isolate x. Because you must do the same thing to both sides, you should subtract 43 from both sides of the inequality.
The +43 and the -43 will cancel out so you just have x on the left side. Then, 50 − 43 = 7. By keeping the inequality the same you get x is less than or equal to
This means Carol's last piece of luggage to check must weigh 7 lbs or less if she wants to avoid extra baggage fees.
Graphing the Inequality on a Number Line
A convenient way to show the solutions to an inequality is by graphing the answer on a number line.
x ≤ 7 means that all numbers less than or equal to 7 are solutions to this problem.
We will put a filled-in dot on the number 7 because 7 is also a solution. Then we will shade the line to the left to include all numbers less than 7.
Because the weight of the luggage can't be negative, we just need to take a look at the positive numbers on the number line.
Checking the Anwser
Now that we've solved the inequality, let's check our answer. First, we need to check the endpoint, or 7. We must plug in 7 for x and see if it makes the inequality true. Is 7 + 43 ≤ 50?
After we simplify our equation, we have 50 ≤ 50. Since 50 = 50, and plugging in 7 for x makes the inequality true, our answer is correct.
Next, you should check one more solution. Let's pick 2. Does plugging in 2 for x make the inequality true? 2 + 43 = 45. So we have 45 ≤ 50. Because this is a true statement, we know that 2 is also a solution to the inequality.
So, to solve inequalities, you can use these steps:
- First, understand the problem. What information is given to you?
- Then, write the inequality.
- After that, use opposite operations to solve, then graph the inequality.
- Finally, check the problem by plugging in the endpoint and one other solution.
Solving and Graphing Example 2
Let's solve and graph one more example. x − 25 ≥ 18.
This time we have subtraction; so in order to do the opposite, we must add 25 to both sides of the inequality.
Make sure to keep the sign facing the same way. The answer is x ≥ 43.
This time we will have an open circle on 43 because 43 is not a solution. Then we draw an arrow to the right towards all numbers that are greater than 43.
Let's get back to Carol. Unfortunately, her last piece of luggage was more than 7 lbs. No problem for Carol...
Solving One-Step Inequalities by Adding or Subtracting exercise
-
Determine the maximum weight of Carol's second suitcase.
HintsUse Opposite Operations:
- Multiplication ($\times~\longleftrightarrow~\div$)
- Division ($\div~\longleftrightarrow~\times$)
- Addition ($+~\longleftrightarrow~-$)
- Subtraction ($-~\longleftrightarrow~+$)
Adding or subtracting doesn't change the sign of the inequality.
When multiplying or dividing by a negative number, you must remember to flip the sign of the inequality.
SolutionConsider the facts then write an inequality to calculate the weight limit of the second suitcase:
- A suitcase weighing $43$ lbs. is already on the scale
- the unknown weight of her second piece of luggage is $x$
- the total weight is $x+43$
- the weight limit is 50 lbs.
We can solve it using Opposite Operations:
$\begin{array}{rcl} x+43&\le&~~~50\\ \color{#669900}{-43} && \color{#669900}{-43}\\ x&\le&~~~~~7 \end{array}$
Carol's second suitcase can weigh $7$ lbs. or less.
Remember: if we add or subtract on both sides of the inequality sign, the sign of the inequality doesn't change directions.
-
Describe how to represent solutions of an inequality on a number line.
HintsYou can transform the inequality using opposite operations.
Use Opposite Operations:
- Multiplication ($\times~\longleftrightarrow~\div$)
- Division ($\div~\longleftrightarrow~\times$)
- Addition ($+~\longleftrightarrow~-$)
- Subtraction ($-~\longleftrightarrow~+$)
Remember that opposite operations must be carried out on both sides of the inequality.
SolutionLet's have a look at the inequality $x+43\le50$.
Subtracting $43$ on both sides, we get $x\le 7$.
The number line shown on the right models the solution set for this inequality.
- Because of the sign $\le$, which means less than or equal to, the circle at $7$ is filled in.
- The arrow is pointing to the left and ends at zero because there's no such thing as negative weights.
-
Find the correct inequalites for the number lines.
HintsTransform each inequality so that you isolate the variable $x$.
When graphing inequalities on the number line, the inequality signs $\le$ or $\ge$ both indicate closed circles while $<$ or $>$ indicate open circles.
SolutionTop Number Line
$\mathbf{x+27\le38}$
- Subtracting $27$ on both sides gives us $x\le 11$.
- Because of $\le$ sign, the circle at $11$ is closed.
- The arrow points to the left.
$\mathbf{x-5<3}$
- Adding $5$ on both sides of the inequality sign gives us $x<8$.
- Because of $<$ sign, the circle at $8$ is open.
- The arrow points to the left.
$\mathbf{x+14\le26}$
- Subtracting $14$ on both sides gives us $x\le 12$.
- Because of $\le$ sign, the circle at $12$ is closed.
- The arrow points to the left.
-
Figure out how much Sue can spend on ice cream.
HintsAll the information needed to solve the problem is included above.
Isolate the variable $x$ using opposite operations.
To check solutions, substitute them back into the inequality.
SolutionTo solve inequalities, we should use the following steps:
- Understand the problem
- Write the inequality
- Solve the inequality
- Check our work
- We know that Paula has $\$20$ in total. She spends $\$12$ on a new shirt. $x$ is the amount for the ice cream.
- So we can say that $x+12$ represents the money Paula spent, and $20$ is her spending limit. This gives us the inequality $x+12\le 20$.
- By subtracting $12$ on both sides of the inequality, we can isolate the variable $x$, giving us $x\le 8$.
- Let's look at two solutions from the number line.
$8+12=20\le20$ $\surd$
$\mathbf{x=4}$:
$4+12=16\le20$ $\surd$
So the girls can spend $\$8$ or less on ice cream.
Naturally, we don't have negative numbers in mind...no one will PAY you to eat ice cream!
-
Decide how much Carol's suitcase can weigh.
HintsThis number line models the solution set of the inequality $x+43\le 50$.
Substitute $x$ with each given value.
Two of the given values are correct solutions for the inequality.
Solution$x$ represents the possible weight of Carol's remaining suitcase.
Subtracting $43$ on both sides leads to $x\le 7$.
All solutions of this inequality can be seen on the right.
Let's check different values for $x$:
$\begin{array}{rclcrcl} x&=&7&&7+43&=&50\le 50 \surd\\ x&=&2&&2+43&=&45\le50 \surd\\ x&=&8&&8+43&=&51\not \le 50\\ x&=&10&&10+43&=&53\not \le 50\\ x&=&12&&12+43&=&55\not \le 50 \end{array}$
-
Solve the inequalities.
HintsFirst, if needed, combine like terms by adding or subtracting values.
Use Opposite Operations:
- Multiplication ($\times~\longleftrightarrow~\div$)
- Division ($\div~\longleftrightarrow~\times$)
- Addition ($+~\longleftrightarrow~-$)
- Subtraction ($-~\longleftrightarrow~+$)
Remember to carry out the opposite operations on both sides of the equation. However, you can combine like terms on one or on both sides of the equation.
SolutionTo solve inequalities, you must isolate the variable $x$. We can do this by Combining Like Terms and using Opposite Operations.
$\mathbf{x+4-7\ge 12}$
$\begin{array}{rclcl} x+4-7&\ge& ~12&&|\text{ Combine Like Terms}\\ x-3 &\ge&~12\\ \color{#669900}{+3}&&\color{#669900}{+3}&&| (-~\leftrightarrow~+) \text{ Opposite Operations}\\ x&\ge&~15\\ ~\\ \end{array}$
$\mathbf{x+12\le 20+14}$
$\begin{array}{rclcl} x+12&\le& 20+14&&|\text{ Combine Like Terms}\\ x+12 &\le&~~~34\\ \color{#669900}{-12}&&\color{#669900}{-12}&&| (+~\leftrightarrow~-) \text{ Opposite Operations}\\ x&\le&~~~22\\ ~\\ \end{array}$
$\mathbf{x+5< 22}$
$\begin{array}{rclcl} x+5&<& ~22\\ \color{#669900}{-5}&&\color{#669900}{-5}&&| (+~\leftrightarrow~-) \text{ Opposite Operations}\\ x&<&~17 \end{array}$